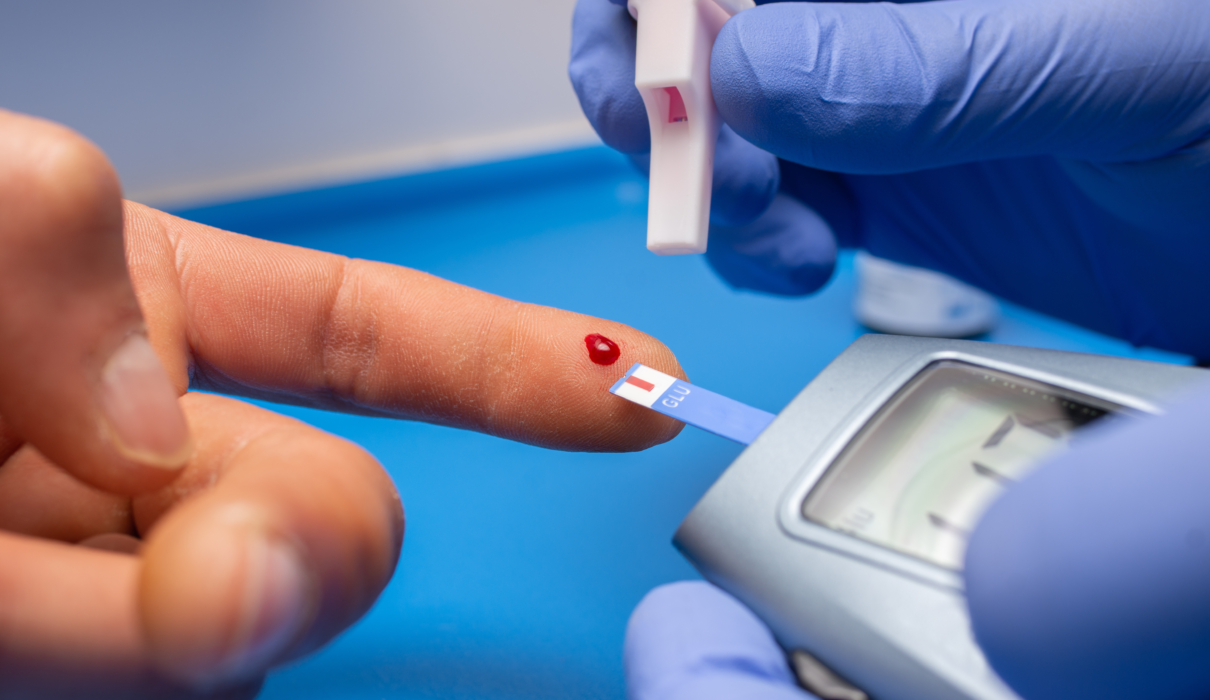
What is a Blood Glucose Test? A blood glucose is a test measures the glucose levels in your blood. Glucose is your body’s main source of energy. insulin hormone helps transfer glucose from your bloodstream to your cells.
Self-testing blood sugar can be an important tool in managing diabetes and preventing complications. You can use a device called a continuous glucose monitor (CGM). Or you can test your blood sugar at home with a portable electronic device called a blood sugar meter. Glucose testing provides useful information for diabetes management as it helps you:
- Monitor the effect of diabetes medications on blood sugar levels,
- Identify blood sugar levels that are high or low.
- Learn how diet and exercise affect blood sugar levels
- Understand how other factors, such as illness or stress, affect blood sugar levels.
Blood sugar monitoring is one of the most important aspects of managing diabetes, especially for people who have type 1 diabetes and those who use insulin. It can indicate you to food , physical activity and insulin dose. That’s why it’s important to check your blood sugar regularly
Regular glucose monitoring is important for people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes.
Too much or too little glucose in the blood can be a sign of a serious condition. High blood glucose levels (hyperglycemia) may be a sign of a disorder that can cause serious, long-term health problems.
There are two main types of blood glucose tests:
Capillary blood glucose test: This test involves a test strip and glucose meter (glucometer), which show your blood sugar level within seconds. Sample is from fingersrick blood.
Venous (plasma) blood glucose test: A sample of blood from a vein (venipuncture). Test made on machines known as analyzers. Test is More accurate with fasting blood glucose test.
When would I need a blood glucose test?
- Your doctor may have ordered routine basic metabolic panel (BMP) or a comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP), which both include a glucose blood test.
- You may have symptoms of hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia ,which could indicate diabetes or another condition.
- If you take a long-term medication that affects your blood sugar levels, like corticosteroids, you may need glucose blood tests to monitor your levels.
The frequency of doing the test: usually depends on the type of diabetes you have and your treatment plan:
- Type 1 diabetes, recommended blood sugar testing 4 to 10 times a day.(Before meals and snacks, Before and after exercise, Before bed, More often if you’re ill, More often if you change your daily routine, More often if you start a new medication).
- Type 2 diabetes, If you take insulin, recommend blood sugar testing several times a day, depending on the type and amount of insulin you take. Testing before meals and at bedtime if you’re taking multiple daily injections. If you manage type 2 diabetes with noninsulin medications or diet and exercise alone, you may not need to test your blood sugar daily.
what are blood glucose test types?

Here are the four most common types of blood sugar:
- Type 2 diabetes (T2D): T2D happens when your pancreas is not able to make enough insulin or your body doesn’t use insulin well (insulin resistance), resulting in high blood glucose levels.
- Type 1 diabetes (T1D): T1D is an autoimmune disease in which your immune system attacks the insulin-producing cells in your pancreas for unknown reasons. Your pancreas can no longer produce insulin. At diagnosis, people with Type 1 diabetes usually have very high blood glucose (200 mg/dL, or higher).
- Gestational diabetes: This condition can develop in pregnant people during the middle of pregnancy, between 24 and 28 weeks. The high blood sugar goes away once the pregnancy is over.
- Hemoglobin A1c: One of the most common diabetes tests. It measures the attachment of glucose molecules to hemoglobin, which is a component of red blood cells. The results indicate the average blood sugar level during 3 months. If this level is higher than 5.7%, it show unusual result
- Random plasma glucose test: (RPG) test also tends to involve a fingerstick or taking blood from an arm vein. The major difference between this test and an FPG test is that an RPG test does not require the person to fast in preparation.
what is the normal range of glucose level in blood?
- Normal Results for fasting blood glucose test, between 70 and 100 mg/dL.
- For random blood glucose test, 125 mg/dL or lower.
- A1C Below 5.7% is considered normal.
- A blood sugar level less than 140 mg/dL is normal.
- Range between 50 and 70 mg/dL for people without diabetes can be “normal” too.
| Test name | Normal levels |
| Random blood sugar | Below 200 mg/dl |
| Fasting blood sugar | Below 100 mg/dl |
| Post prandial blood sugar | Below 140 mg/dl |
| HBA1C | Below 6.0 % |
Normal blood glucose levels by age:
Before meals, your blood sugar should be:
From 90 to 130 mg/dL for adults.
From 90 to 130 mg/dL for children, 13 to 19 years old.
From 90 to 180 mg/dL for children, 6 to 12 years old.
From 100 to 180 mg/dL for children under 6 years old.
After meals (1 to 2 hours after eating), your blood sugar should be:
Less than 180 mg/dL for adults.
At bedtime, your blood sugar should be:
From 90 to 150 mg/dL for adults.
From 90 to 150 mg/dL for children, 13 to 19 years old.
From 100 to 180 mg/dL for children, 6 to 12 years old.
From 110 to 200 mg/dL for children under 6 years old.
When glucose level in blood considered fatal?
If your blood glucose is too high for too long, it can cause serious problems ,such as diabetic coma.
A diabetic coma could be developed when your blood sugar gets too high :600 mg/dL or more, making you very dehydrated. If you go into a diabetic coma, you’re alive, but you can’t wake up or respond to any stimulation. If it’s not treated, it can lead to death.
what is the normal blood sugar for pregnant?


- Before a meal: 95 mg/dL or less
- One hour after a meal: 140 mg/dL or less
- Two hours after a meal: 120 mg/dL or less.
Importance of measuring high blood glucose for pregnant: High blood glucose can harm your baby even before you know you are pregnant. You also have a greater chance of getting preeclampsia (toxemia), which is in high blood pressure and too much protein in your urine during the second half of pregnancy Which can cause serious or life-threatening problems for you and your baby.
The extreme high level of blood glucose: Hyperglycemia occurres, when blood sugar levels are high : above 180 to 200(mg/dL).
The extreme low level of blood glucose: Hypoglycemia developes , when fasting blood sugar is: 70 (mg/dL) or below.
What is the normal blood glucose levels for children?
- Children less than 5 years old: 70-180 mg/dL
- 5 years and older: 71-150 mg/dL
- At bedtime: 101-200 mg/dL.
- The A1C goal is 7%.
What is the glucose level that diagnosed as hypoglycaemia?
Low blood glucose levels (hypoglycemia) are common among people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Without treatment, severe low blood sugar can lead to major health diseases, including seizures and brain damage. Hypoglycaemia is defined as a glucose level of less than 70 mg/dL or slightly higher.
What is the glucose level that diagnosed as hyperglycaemia?
High blood sugar, or hyperglycemia, is characterized by a glucose level between 100 to 125 mg/dL during fasting.
(In 2014, 8.5% of adults aged 18 years and older had diabetes. In 2019, diabetes was the direct cause of 1.5 million deaths and 48% of all deaths due to diabetes occurred before the age of 70 years.{Global Burden of Disease Collaborative Network. Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Results. Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation. 2020}).